Population Class 9 Important Questions Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the organisation which provide us with information regarding the population of our country?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
The Census of India
Question 2.
State the position of India in terms of population size?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
Second
Question 3.
State the total population of India according to the 2011 census?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
Around 1210.2 million
Question 4.
Which is the?
Year of Question :(2018)
- (i) most populous state of India
- (ii) The least populous state of India
Answer:
- (i) Most populous - Uttar Pradesh
- (ii) Least populous - Sikkim
Question 5.
State the total percentage which India accounts to the total population of the world?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
About 16.7 per cent
Question 6.
What is Indias share in the-total area of the world?
Year of Question :(2017)
Answer:
Around 2.4 per cent
Question 7.
What is the annual growth rate of population of India?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
Approximately 1.58 per cent
Question 8.
Which is the most densely populated country of the world?
Year of Question :(1985)
]
Answer:
India, about 382 persons per sq km
Question 9.
Which is the most populated country, in terms of population size?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
China.
Question 10.
How would you define the term density of population?
Year of Question :(2016)
Answer:
Number of persons living per unit of area (per sq km)
Question 11.
What is the growth of population?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
It refers to the change in the number of inhabitants of a country/territory during a specific period of time
Question 12.
Growth of population is expressed in two ways. Mention?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
- Absolute number
- Percentage change
Question 13.
Define the annual growth rate of population?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
It is the rate of increase of population in the base population
Question 14.
Name the state having the highest and the lowest density of population?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
The state having the highest density of population is Bihar (1102 persons per square km) and the lowest is Arunachal Pradesh (17 persons per square km). Both these are approximate figures
Question 15.
State two factors which affect the distribution of the density of population?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
- Climate
- Natural resources
Question 16.
State any two implications of the high density of population?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
Question 17.
Give two reasons responsible for unfavourable sex-ratio?
Year of Question :(2013)
Answer:
- Women are often done to death by dowry seekers
- Lack of education and orthodox customs also go against women folk
Question 18.
What do you understand by the growth rate?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
Thegrowth rateis the annual percentage increase in the population of a country
Question 19.
Why is the North India, plain thickly populated? Give two reasons?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- The soil of the region is fertile
- There are large number of factories in this area which provide employment opportunities
Question 20.
Why is there less population in Rajasthan?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
- The soil in Rajasthan is less fertile
- The climate of the region is of extreme type
Question 21.
Define the term birth rate?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
The birth rate is the proportion of the number of births in a place in particular duration to the total population, usually expressed as a quantity per thousand people per year
Question 22.
What is death rate?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
The number of deaths per thousand persons in a year is called as the death rate
Question 23.
What is migration?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
It is the movement of people across regions and territories
Question 24.
What is internal migration?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
The movement of people within the country
Question 25.
What is external migration?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
The movement of people across the countries
Question 26.
What is the dependent ratio of population?
Year of Question :(2017)
Answer:
Dependent ratio is the ratio between the economically working population and the dependent population
Question 27.
The sex ratio in rural areas is some what higher than in urban areas. Give one possible cause for it?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
Migration of male members to the cities in search of jobs
Question 28.
Migration is an important determinant of population change. Give reason?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
Migration changes not only the population size but also the population composition of urban and rural populations in terms of age and sex composition
Question 29.
What is age composition?
Year of Question :(2016)
Answer:
It refers to the number of people in different age groups in a country
Question 30.
What is sex ratio?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
The number of females per 1,000 males in the population
Question 31.
Who is literate?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
According to the Census of2001, a person aged 7 years and above who can read and write with understanding in any language, is treated as literate
Question 32.
What is occupational structure?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
The distribution of the population according to different types of occupation is referred as the occupational structure
Question 33.
What is census?
Year of Question :(2013)
Answer:
The census is a count of population of a country. In India, it takes place after every ten years. The last census in India was held in 2011. It is an enquiry based on questionnaire
Question 34.
Give two reasons for the migration of people from the rural to urban areas in India?
Year of Question :(2012)
Answer:
- Rising population in rural areas.
- Lack of demand for labour in agriculture
Question 35.
Name any two states with high density of population?
Year of Question :(2011)
Answer:
Question 36.
Name any four states with low density of population?
Year of Question :(2010)
Answer:
- Mizoram
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Nagaland
- Manipur
Question 37.
What is the sex ratio in India?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
According to 2011 Census, the sex ratio in India is 940
Question 38.
What is the literacy level in India?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
74.04 per cent (2011 Census).
Male-82.14 Female - 65.46
Question 39.
What is life expectancy in India?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
Around 65.48 years
Population Class 9 Important Questions Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
"The people are important to develop the economy and society ."Explain?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
- The people make and use resources and are themselves resources with varying quality
- It is the point of reference from which all other elements are observed and from which they derive significance and meaning
- "Resources, calamities and disasters are all meaningful only in relation to human beings. Their numbers
distribution, growth and characteristics or qualities provide the basic background for understanding and appreciating all aspects of the environment
- Human beings are producers and consumers of earths resources
- Therefore, it is important to know how many people are there in a country, where do they five, how and why their numbers are increasing and what are their characteristics
Question 2.
"Assam and most of the Penin-sular states have moderate population densities." Give three reasons?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
- The region has hilly,dissected and rocky terrain
- The region receives moderate to low rainfall
- The region has shallow and less fertile soil
Question 3.
Mention the process of change of population?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
- Birthrate
- Death rate
- Migration
Question 4.
What are the major factors responsible for internal migration?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
In India, most migrations have been from the rural to the urban areas because of the "push" factor in rural areas. These are adverse conditions of poverty and unemployment in the rural areas and the "pull" of the city in terms of increased employment opportunities are better living conditions
Question 5.
What is occupational structure? Explain?
Year of Question :(2013)
Answer:
Occupational structure refers to the distribution of work force among different occupations. Different occupations can be classified into three groups
- (i) Primary occupations
- (ii) Secondary occupations
- (iii) Tertiary occupations
- (i) Primary Producers or Occupations: Those who grow natural products like crops, etc. and are mainly engaged in agriculture and allied activities
- (ii) Secondary Occupations: Those who are producing products with the help of machines like textiles, construction, etc
- (iii) Tertiary Occupations: Those who provide services like education, health services, banking, insurance, etc
About 64 per cent population of India is still engaged in primary sector
Question 6.
Write short notes on the age composition of population and dependency?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
The age composition of population refers to the number of people in different age groups in a country. It is one of the most basic characteristics of a population.
The age composition of population is expressed in three broad categories
- Children below the working age (below 15 yrs): They are economically unproductive, and need to be provided with food, clothing, education and medical care
- Persons in the working age (15 to 59 yrs): They are economically productive and biologically reproductive. They comprise the work population
- Old persons above the working age (above 59 yrs): They can be economically productive, but need care
Anyone, who is engaged in work and has the ability to do so is the part of the working population. The dependent population is either in the age group of below 15 years or in the age group of over 59 years
Question 7.
What is the difference between internal and external (international) migration?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:

Question 8.
What is sex ratio? Give two reasons responsible for an unfavourable sex ratio in India?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
The number of females per thousand of males is called the sex ratio.
In 1901, the ratio was 1000: 972 but it dropped to 1.000:940 in 2011. Main causes of the change of ratio are
- Low social, economic and political status of women
- Dowry system is also responsible for this
- Parents also feel insecure if a girl child is bom
Question 9.
What are the significant features of the National Population Policy 2000?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
- National Population Policy is a policy adopted by the Government of India in 2000
- It aims at stabilising the population by 2045
- It also lays emphasis on the economic growth, social development and environment protection
- The Policy states that it will achieve this goal by raising the age of marriage, making school education free and compulsory upto the age of 14 years and reducing dropouts at the primary and the secondary levels
Population Class 9 Important Questions Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the main cause of the rapid population growth in India?
Year of Question :(2015)
Answer:
- High Birth Rate and Low Death Rate: From 1921 to 2001, the death rate has fallen from 42.6 to 8.7 per thousand while the birth rate fell from 49.2 to 26.1 per thousand
- Poverty: Poor people have to spend little on the upbringing of their offsprings. Besides, the children supplement the family income
- Child Marriage: Early marriage is a common feature in India. About 90 per cent of girls are married in the age group of 15-20 years
- Low status of women; In India women have a low social status. They are treated merely as child producing machines
- Illiteracy: Rate of illiteracy of 35 per cent is pretty high in India. Illiterate persons fail to understand the significance of family planning
Question 2.
Explain the process of population change?
Year of Question :(2014)
Answer:
There are three main processes of change of population: birth rates, death rates and migration. The natural increase of population is the difference between birth rates and death rates
- Birth rate: Birth rate is the number of live births per thousand persons in a year. It is a major component of growth because in India, birth rates have always been higher than death rates
- Death rate: Death rate is the number of deaths per thousand persons in a year. The main cause of the rate of growth of the Indian population has been the rapid decline in death rates. Till 1980, high birth rates and declining death rates led to a large difference between birth rates and death rates resulting in higher rates of population growth. Since 1981, birth rates have also starred declining gradually, resulting in a gradual decline in the rate of population growth
- Migration - The third component of population growth is migration. Migration is the movement of people across regions and territories. Migration can be internal (within the country) or international (between the countries). Internal migration does not change the size of the: population, but influences the distribution of population within the nation. Migration plays a very significant role in changing the composition and distribution of population
Question 3.
Write an essay on the population distribution in India pointing out the geographical factors influencing the same?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
Distribution of population: The average density of population in India according to 2011 Census was about 382 persons per sq. Km
- Low density: The states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Aruna-chal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Tripura, Meghalaya, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh have very low to low population density. Rugged terrain and unfavourable climatic conditions are mainly responsible for the sparse population in these areas
- Moderate density: The bulk of the peninsular blocks and Assam have a moderate density of population. Distribution of population is influenced here by the rocky nature of the terrain, low to moderate rain, and shallow and less fertile soil
- High density: The Northern Plains, Tamil Nadu and Kerala have high to very high density of population because of the plain terrain, rich and fertile soil, abundant rainfall and moderate climate
Population Class 9 Important Questions Higher Order Thinking Skills (Hots) Questions
Question 1.
Study the given figure carefully, and answer the following questions?
Year of Question :(2018)
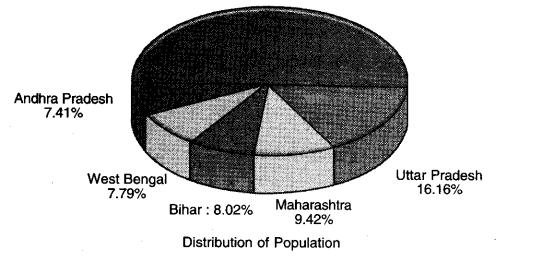
- (i) Which state has the highest share in population
- (ii) Which state hasthe lowest share in population
- (iii) What is the share of Bihar in the Indias population
Answer:
- (i) Uttar Pradesh
- (ii) Andhra Pradesh
- (iii) 8.02%
Question 2.
Study the above data carefully and answer the following questions:
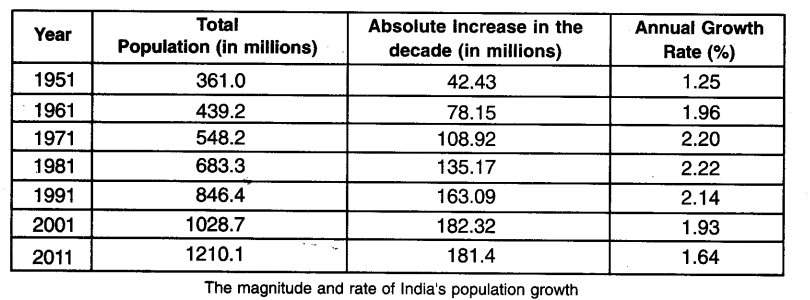 The magnitude and rate of Indias population growth?
The magnitude and rate of Indias population growth?
Year of Question :(2015)
- (i) What was Indias population in 1951
- (ii) What was Indias population in 2011
- (iii) What was absolute increase in Indias Population from 2001 to 2011
- (iv) Which decade has lowest annual growth rate
Answer:
- (i) 361 million
- (ii) 1210.1 million
- (iii) 1210.1 - 1028.7 = 181.4 million
- (iv) 1951
Question 3.
Study the given figure carefully and answer the following questions?
Year of Question :(2018)
- (i) Which age group has the maximum share in the population
- (ii) What do you mean by the working population
- (iii) What is Indias working population

Answer:
- (i) 15-59 years age group, i.e., 58.7per cent
- (ii) Anyone who is engaged in productive work and has the ability to do so is a part of the working population
- (iii) 58.7%
Question 4.
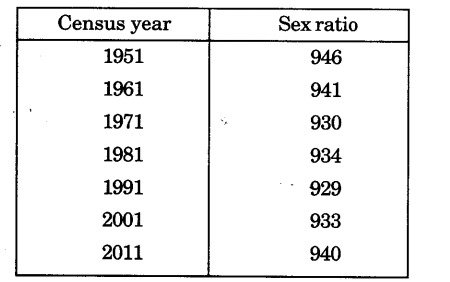 ?
?
Year of Question :(2018)
- (i) What is sex ratio
- (ii) What is Indias sex ratio in 2011
- (iii) Is sex ratio in the country favourable to females
- (iv) Give one reason for unfavourable sex ratio in India
Answer:
- (i) Number of females per 1,000 males in the population
- (ii) 940 females per 1000 males
- (iii) No, it is unfavourable to females
- (iv) Illiteracy
Population Class 9 Important Questions Value Based Questions
Question 1.
Kerala has a sex ratio of 1084. Which moral value this data provides us?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
There is gender equality
Question 2.
The literacy rate in India is 74.40,82.14 for males and 65.46 for females. What does this indicates?
Year of Question :(2011)
Answer:
Gender inequality
Question 3.
Mention any two ways to improve the status of women in India?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
- Reservation of seats in the Parliament for women
- Improve literacy rate
Question 4.
Suggest any three ways to control the rapid growth of population in India?
Year of Question :(2016)
Answer:
- Spread of education
- Late marriage
- New population policy
Question 5.
Who is treated as literate in India? What is importance of literacy?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
According to the census of 2011, a person aged 7 years and above who can read and write with understanding in any language, is treated as literate.
Importance
- Only an informed and educated citizen can make intelligent choice and undertake research and development projects
- Literate citizens become human resource
Question 6.
"The percentage of population that is economically active is an important index of development."Explain?
Year of Question :(2017)
Answer:
- Economic growth is directly dependent on human resources
- In countries like a very high percentage of population is economically active so these countries have achieved a very high economic growth rate
- In most of the developing nations the dependency ratio is very high so economic growth rate remains low
Question 7.
"Health situation in India is still a cause for serious concern". Give reasons?
Year of Question :(2018)
Answer:
- Public health facilities only for few: At present, less than 20 per cent of the population utilises public health facilities. One study has pointed out that only 38 per cent of the PHCs have the required number of doctors and only 30 per cent of the PHCs have sufficient stock of medicines
- Poor health facilities in rural India: Though 70 per cent of Indias population lives in rural areas, only one-fifth of its hospitals are located in rural areas. Rural India has only about half the number of dispensaries.
Poor health status for women: More than 50 percent of married women between the age group of 15 and 49 have anaemia and nutritional anaemia caused by iron deficiency, which has contributed to 19 percent of maternal death
Important Questions and Answers
Question1.
What is Population, and why is it important?
Answer:
- Definition of Population:
- Population refers to the number of "people" living in a particular area
- Importance:
- Resource Utilization: Humans create and use resources
- Economic Development: People contribute to "society" and the "economy."
- Impact on Environment: Natural events like "floods" or "tsunamis" become significant when they affect populated areas
- Social Structure: Population data helps understand social needs like health, education, and employment
Question2.
Describe Population Size and Distribution in India?
Answer:
- Population Size:
- As per the 2001 Census, Indias population was 1.028 billion
- India has 16.7% of the worlds population but only 2.4% of the worlds land area
- Population Distribution:
- Most Populous States: "Uttar Pradesh" with 166 million people, followed by "Maharashtra,"
- "Bihar," "West Bengal," and "Andhra Pradesh."
- Least Populated Regions: "Lakshadweep" and "Sikkim."
Question3.
What factors affect the density of Population in India?
Answer:
- Population Density: Number of people per square kilometer
- High Population Density:
- Found in the "Northern Plains" and "Kerala" due to fertile soil and adequate rainfall
- Low Population Density:
- States like "Arunachal Pradesh" (13 persons per sq. km) have low density due to rugged terrain and poor soil
- Moderate Density:
- States like "Assam" and Peninsular states have moderate density due to average rainfall and diverse landforms
Question4.
Explain the concept of Population Growth?
Answer:
- Population Growth: Increase in the number of inhabitants over a period
- Absolute Growth:
- The actual increase in population numbers over time
- Example: Indias population grew from 361 million in 1951 to 1.028 billion in 2001
- Annual Growth Rate:
- Expressed as a percentage. For instance, a 2% growth rate means 2 new people for every 100 existing people
- Trends:
- 1951-1981: Rapid growth with high birth rates and declining death rates
- 1981 onwards: Gradual decline in growth rate due to lower birth rates
Question5.
What are the Main Components of Population Change?
Answer:
- Birth Rate:
- Number of births per 1,000 people per year
- Higher birth rates contribute significantly to population growth
- Death Rate:
- Number of deaths per 1,000 people per year
- Declining death rates due to better healthcare lead to population growth
- Migration:
- Internal Migration: Movement within India, usually from rural to urban areas
- International Migration: Movement between countries, which can affect population composition
Question6.
What is the Age Composition of Indias Population?
Answer:
- Categories:
- Children (Below 15 years): Depend on adults for food, education, and healthcare
- Working Age (15-59 years): Economically productive and contribute to society
Aged (Above 59 years): May or may not be active in the workforce
- Dependency Ratio: High numbers of children and aged people increase dependency on the working-age group
Question7.
What is the Literacy Rate in India, and why is it important?
Answer:
- Definition:
- A "literate" person can read and write in any language with understanding
- Literacy Rates (2001 Census):
- Overall: 64.84%
- Male: 75.26%
- Female: 53.67%
- Importance:
- Higher literacy improves the ability to make informed decisions, enhances job opportunities, and contributes to economic growth
Question8.
Explain the National Population Policy (NPP) 2000?
Answer:
- Objective: To stabilize population growth and improve health and family welfare
- Goals:
- Free and compulsory education up to 14 years
- Reduce "Infant Mortality Rate" to below 30 per 1,000 live births
- Universal immunization for children
- Promote delayed marriage and childbearing
- Focus on Adolescents:
- Address "nutritional needs" and awareness about "health and family planning."
Educate adolescents on the risks of unprotected sex and promote awareness of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)